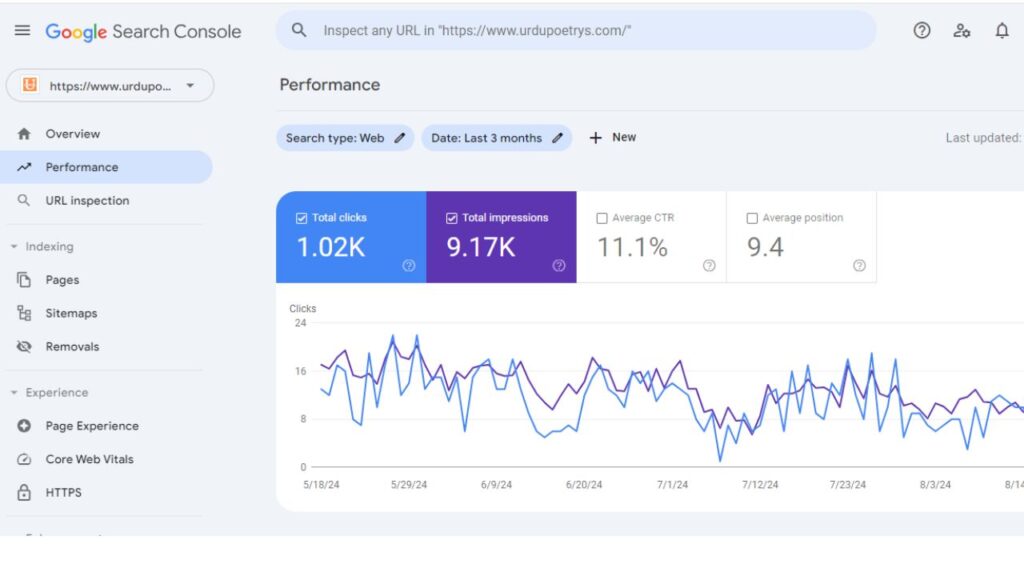
If you own a website, knowing how it performs in search results is essential.
Google Search Console (GSC) is one of the most powerful free tools you can use to track performance, troubleshoot issues, and improve your visibility in search results.
Whether you’re new to SEO or just starting a blog, understanding GSC can make a big difference in how your site grows.
This detailed guide is designed primarily for beginners however also useful for advance users and will cover everything you need to get started, from setup to using its features effectively.
What Is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console is a free service provided by Google that helps you understand how your website appears and performs in Google Search. It acts like a dashboard for your website’s relationship with Google, giving you data and tools to:
- See which keywords and queries drive traffic to your site.
- Monitor how your pages appear in search results.
- Identify indexing and coverage issues.
- Improve your website’s performance and user experience.
In short, GSC tells you what Google knows about your website.
Why GSC is Important for Website Owner
Even if you’re not an SEO expert, Google Search Console can give you insights that help you make better decisions. Here are a few reasons why it’s important:
- Search visibility: Understand which keywords are performing and which need work.
- Error tracking: It alerts you if there are broken pages, mobile usability issues, or security problems.
- Indexing insights: You can see which pages Google has indexed and which are excluded.
- Content insights: Learn what content resonates with your audience.
- Backlink data: See which external sites link to your content.
- Performance metrics: Learn about impressions, clicks, and average positions of your pages.
Think of GSC as a direct line to how Google sees your website.
How to Set Up Google Search Console
Adding your website to Google Search Console is the first and most important step before you can start analyzing data and optimizing your site. Below is a detailed, step-by-step explanation to make the process simple for beginners.
Step 1: Sign In to Google Search Console
- Go to search.google.com/search-console.
- Click on the Start Now button.
- Log in with your Google account. If you do not have one, you’ll need to create a Google account first.
Step 2: Choose a Property Type
When you click Add Property, you’ll see two options, Domain and URL Prefix:
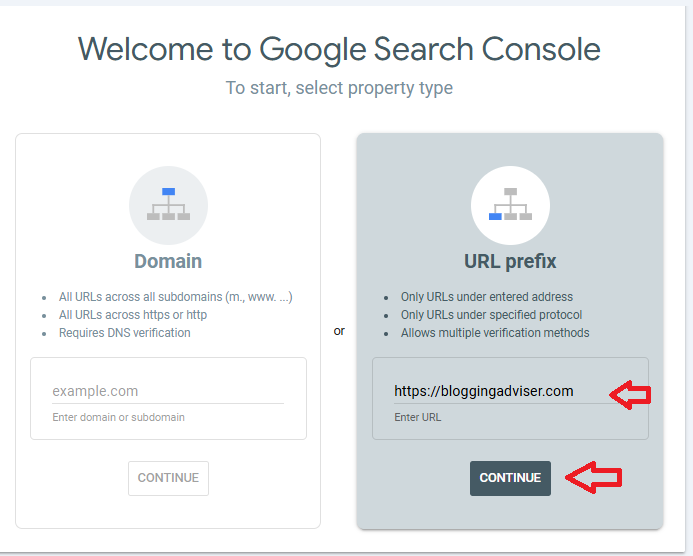
1. Domain Property: Covers your entire domain, including all subdomains (e.g., blog.yoursite.com) and protocols (http and https).
Example: example.com
2. URL Prefix Property: Covers only URLs that start with a specific prefix.
Example: https://www.example.com
Which one should you choose?
- Domain property is recommended if you want complete coverage of your site.
- URL prefix is useful for specific projects or smaller sites.
Step 3: Verify Ownership
Verification ensures that you own or manage the site. Google offers several verification methods:
1. DNS Record (Recommended for Domain Property)
- Copy the TXT record provided by Google.
- Log in to your domain registrar (e.g., GoDaddy, Namecheap).
- Add the TXT record to your DNS settings.
- Save and return to GSC to click Verify. It may take a few minutes to propagate.
2. HTML File Upload (For URL Prefix)
- Download the HTML verification file.
- Upload it to the root directory of your website using an FTP client or your hosting panel.
- Return to GSC and click Verify.
3. Meta Tag Verification (For URL Prefix)
- Copy the meta tag provided.
- Paste it into the
<head>section of your website’s homepage. - Save changes and click Verify.
4. Google Analytics or Tag Manager
- If you already use Google Analytics or Tag Manager, you can verify your site through these platforms without additional steps.
Step 4: Submit Your Sitemap
Once your site is verified, the next step is to help Google discover your content faster:
- Find your sitemap (commonly
yoursite.com/sitemap.xml). - In GSC, click Sitemaps from the left-hand menu.
- Enter your sitemap URL and click Submit.
Step 5: Confirm Successful Setup
- After verification and sitemap submission, you’ll start seeing data in GSC within a few days.
- Check the Coverage and Performance reports to ensure everything is working correctly.
Pro Tips
- Always verify ownership using the most secure method, especially if you’re working with client sites.
- If you change hosting or domain settings, you might need to re-verify.
- Keep your property list updated if you manage multiple sites.
By completing these steps, you’ll give Google a clear signal that your website is active and ready to be indexed. This is the foundation for using all the features in Google Search Console effectively.
Key Features of Google Search Console
Here are the main sections beginners should understand:
1. Performance Report: Shows metrics like:
- Clicks: How many times users clicked your site from search results.
- Impressions: How often your site appeared.
- Average Position: The average ranking of your pages.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Percentage of impressions that turned into clicks.
Example 1: If your article “Best WordPress Plugins” has 1,000 impressions but only 20 clicks, the CTR is low. This could mean your title or meta description needs improvement.
Example 2: If your blog post on “best SEO tools” gets 300 clicks but appears in position 25, you know it needs optimization
2. URL Inspection Tool: Lets you check how Google sees a specific page. Enter any URL to see:
- Whether it’s indexed.
- When it was last crawled.
- Issues preventing it from appearing in search.
Useful when you publish a new page and want to ensure Google knows about it.
3. Coverage Report: it shows:
- Indexed pages.
- Errors (404s, redirects).
- Warnings (pages with issues).
- Excluded pages (intentionally blocked or duplicate content).
Example: If you notice 10 important blog posts are excluded, it’s time to check why.
4. Enhancements and Experience Reports: Offers insights into mobile usability, Core Web Vitals, and more:
- Core Web Vitals: Measures loading speed, interactivity, and visual stability.
- Mobile Usability: Highlights issues that could hurt your site’s mobile performance.
These reports help ensure your website delivers a good experience, which affects rankings.
5. Links Report: It shows
- Internal links: Pages within your site linking to each other.
- External links: Other websites linking to you.
- Top linked pages and anchor text.
Backlinks are important for SEO authority, so this data is valuable for outreach and strategy.
How to Use GSC Data to Improve Your Site
Data is only useful if you act on it. Here’s how beginners can use GSC insights:
- Identify high-performing keywords: See which keywords bring traffic and build more content around them.
- Fix errors quickly: Address coverage issues or indexing problems so search engines can crawl your site properly. Resolve 404 errors or improve pages marked “Crawled – currently not indexed.”
- Improve CTR: Test better titles and meta descriptions.
- Monitor backlinks: Identify which pages attract the most links and replicate their success.
- Optimize user experience: Core Web Vitals can guide you to improve site speed and mobile performance.
Common Beginner Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Ignoring verification methods: Always ensure your property is verified; otherwise, you won’t see data.
- Not checking reports regularly: Monthly or even weekly checks can catch problems early.
- Skipping sitemap submission: A missing sitemap can slow indexing.
- Overlooking mobile usability: With mobile-first indexing, mobile errors can cost you traffic.
Troubleshooting Tips
- “Couldn’t Fetch Sitemap” Error: Check your sitemap URL and ensure it’s accessible. Test it in a browser.
- Indexing Delay: New content can take time to appear. Use the URL inspection tool to request indexing.
- Duplicate Content Issues: Use canonical tags to signal preferred pages.
Best Practices for Beginners
- Keep your website clean and organized; broken links and errors hurt SEO.
- Use descriptive URLs and clear headings.
- Write quality content; GSC data is only as good as your content.
- Link internally to help Google understand your site structure.
Final Thoughts
Google Search Console is a must-have tool for anyone serious about building a website. It not only helps you understand what’s working but also points out what needs attention. By checking it regularly, you can make data-driven decisions and grow your site faster.